Cable Management Systems(CMS) in data center
Have you ever thought about the number of connections required in a data center? Let it be power cables or networking cables. It depends on the number of connections required in each device, electric connections required for each of the racks or devices. The amount of cables to be pulled is massive, right? Have you ever seen that such a cabling mess in any of the standard data centers? We will never see an ugly picture in well-maintained data centers. So what would be the system used for this? Well, there is a number of dependencies for the answers to this. One of the major things would be with the help of Cable Management Systems(CMS). Cable management systems (CMS) provide a structured, organized solution for power and communications cable installations within a broad range of enclosure applications—from two- or four-post open-frame racks to wall-mount and free-stand cabinets. So the understanding of components used in the cable management system(CMS) is inevitable for a data center. Based on this information we can apply different components in different areas.
Cable Management Systems(CMS) Design Considerations
Industry trends
IT innovations occur every day. thus, the ideal CMS solutions are designed to facilitate easy cable moves, adds and changes (macs) within its environment, allowing fast updates while saving valuable resources. Hence to understand this, we must develop the CMS by understanding the future growth of the industry.
Cable type
Generally, there can be two types of cables used within the data center which are for carrying electricity and another one is for connectivity(Fiber or Copper) hence these cables can be of different sizes.
Cable performance
CMS solutions should reduce stresses, bends and pressure points, which can lead to poor performance. In particular, weight from larger diameter cables can create these problem points, so CMS solutions should be designed for even distribution of the cable weight.
Space and organization
CMS solutions for cables external to a cabinet and within a cabinet are modular in design and can be pieced together to fit any space. Cables can be strung low, high and in-between, with runs located above cabinets, up and down walls and under
raised floors(White Space Overhead Data Cabling or White Space Raised Floor applications). You should decide the location of each cable type and which area these cables types will be fixed.
Cable Ingress/ Egress points
Ingress and egress points are the points where the cabling enters and exits a cabinet—can be overhead or below the floor. Designers must plan for all current ingress/egress points and allow room for future cable installations.
Cabinet airflow requirements
Airflow cubic feet per minute (CFM) measurements should exceed requirements to keep critical electronic components cool. We should make sure that the cabling should be designed to maximize airflow. For example, when you are operating CRAC within raised floor structure and having an underfloor cabling structure this can actually impact the airflow. In this situation, the best recommended is for overhead cabling.
Pathways and Containments
One of the most critical factors of data center operation is the meticulous design and planning of the pathways and containment systems that accommodate the power and data cabling. Poorly planned and installed cabling networks rarely improve over time, in fact, continued degradation tends to become the norm. Continued degradation will affect airflow and could lead to equipment overheating. Industry standards define pathways and containment as,
Pathways -the space in which containment systems will be installed e.g. plenums, risers, underfloor, etc.
Containment -the physical system into which cables are installed e.g. cable tray, cable basket, trunking, and conduits, etc.
Selection of Pathways
Datacenter cabling pathways will be either Underfloor or Overhead.
Underfloor – mounted on brackets permanently fixed to the floor slab This has been a preferred option in the past due to it being out of sight:
o Advantage -The raised floor plenum allows for plenty of space and an opportunity to install containment and cabling out of sight
o Disadvantage -No visual indicators to the state of the installation
Overhead – Suspended from the ceiling
Overhead cable containment routes are becoming more popular due to advances in the way the hot air is being exhausted from the data hall, and therefore would not have a detrimental effect on the cables:
o Advantage -Significant cost savings can be realized in not having to install raised access flooring
o Disadvantage -a more complex and time-consuming installation process
Containment – Cable Trays for effective CMS
Cable trays are containment components used for cable support consisting of a base with integrated side members or a base connected to side members. There are multiple types of cable trays used in the data center. In fact, the most lengthy and slightly harder solution used is nothing but the Cable Trays. Most cable tray systems are fabricated from a corrosion-resistant metal (low-carbon steel, stainless steel or an aluminum alloy) or from metal with a corrosion-resistant finish (zinc or epoxy). Cable trays are broadly known for their dependability, adaptability, safety, reliability, low maintenance need, easy installation and long operating life.
Installation Standards of Cable Trays
There are some of the major standards to be followed for each cable tray installations. Some of the major standards to be met for this installation is as below,

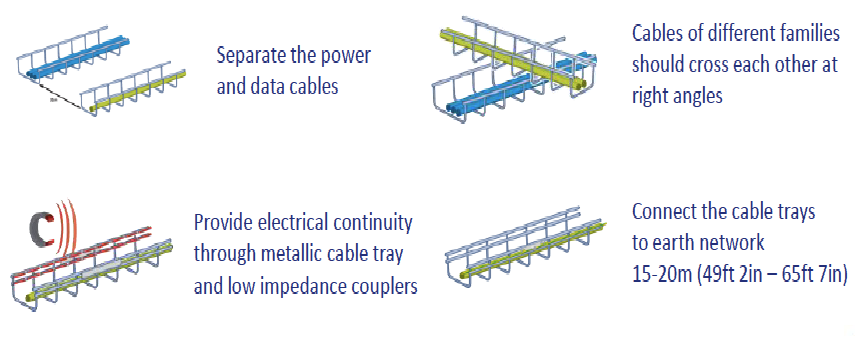
So what are the other things to be considered before choosing the pathways for CMS? Some of the main considerations are,
- Earth/bond/ground correctly
- Label pathways
- Label cables at both ends
- Protect bend radius of copper data and fiber cables
- Maintain separation from power cables
- Keep the integrity of fire barriers
Let us have a look into some of the most commonly used cable trays within data centers,
1) Ladder rack cable trays
As the name indicates, these types of cable trays are having a Ladder shape which you can see as per the below picture. Ladder trays are prefabricated metal structures that consist of two side rails connected by individual transverse members or rungs. Cope Ladder tray can withstand heavy rigor and harsh environments with heavy hot-dip galvanized steel, fiberglass, and aluminum options.

Features,
- Ladder cable trays have a strong and robust structure for laying cables in any sizes and it has high loading capacities.
- Ladder cable trays resist corrosion, heat due to hot-dipped galvanized, pre-galvanized, powder-coated surface.
- Excellent air-ventilation property due to the spacious ladder type.
- Used in all locations except elevator shafts.
- Various components connected by accessories.
- Beautiful structure. Ladder cable trays side-channel types include C channel, I-beam channel.
- Longer service life.
Ladder tray is the most common and the most economical type of tray, also providing maximum ventilation for cabling. Ladder tray systems are a cost-effective alternative and allow for easy installation of cables by electricians as well as future access for adding or removing cable runs.
2) Solid bottom cable tray or Channel Cable Tray
As the name implies the design of solid bottom cable trays is solid. These are robust designs which are covered the tray systems from all sides. Hence the cables that you are lying will be most secured among all other cable tray systems. You can choose to have these cable trays with a cover or without cover.

Channel type cable tray has enclosed cover to protect cables from sunlight, falling objects, dust, and water or other liquid.
Features
- Channel cable trays are fully enclosed and they can protect cables from heat, dust, and water.
- Electro galvanized, hot-dipped galvanized surface makes channel cable trays resist corrosion, rust, and chemicals.
- Channel cable trays have fine fire resistance property.
- High loading capacity to support cables.
- Simple structure and easy to install with corresponding accessories.
- Long service life.
3) Perforated or trough cable tray
Perforated cable tray is a kind of cable tray with holes on the bottom sheet and side rails for laying power and signal cables. Compared with channel cable tray, perforated cable tray has holes on the bottom to help ventilate the cables. These are generally used for moderate heat generating electrical or telecommunication applications.

Features
- Strong structure for carrying all types of cables.
- Perforated cable trays have holes on the bottom to provide enough ventilation and position for cable lines.
- Anti-corrosion, fire, moisture due to the pre-galvanized, hot-dipped powder coated, epoxy coated finish.
- Excellent heat dispersion.
- Safe and smooth edge protects cable lines from scratch.
- Strong enough to withstand short circuit.
- Flexible, easy and quick installation.
- Special construction design allows cable trays to go anywhere.
- Easy to maintain and long life span.
4) Spine cable tray
Center Spine Cable Tray is an easily installed cable support system designed to provide safety, reliability, and flexibility for future expansion. Field modifiable fittings combine to allow installers to easily maneuver cable pathways around obstructions and changes in elevation.

5) Wire mesh tray (basket)
Wire mesh cable tray, also called basket cable tray, is a kind of cable tray made of stainless steel wires by welding wires together, forming a basket-like mesh. Wire mesh cable trays provide a quick solution to supporting large quantities of cables in data centers, network equipment rooms and places where there is complex machinery.

One characteristic that defines a wire basket is the amount of open space in it, which permits continuous airflow to help prevent heat buildup. In addition, this unique open design prevents the buildup of dust, contaminants and bacterial proliferation.
Features,
- Wire mesh cable trays have a high strength to support large quantities of network cables.
- Resist corrosion, heat because of pre-galvanized, hot-dipped galvanized, powder coated surface treatment.
- Open design makes cables move, ventilate smoothly, decreasing the collection of debris, dust.
- Can be cut and formed to create smooth curved transitions around obstacles.
- Available in many sizes depending on different uses.
- No sharp edges and prevent injuries and damage to cables.
- Easy and fast installation with accessories.
6) Wireway with “fully gasketed” cover
We can say that this is the advancement of channel cable trays. These are generally known as Square-Duct Wireways due to its shape. Wireway is designed to protect electrical wiring from dust, dirt, oil, and water. It is also designed to carry electrical feeders, branch circuits, and other groups of conductors. Most sections and fittings are completely open on one side so wires and cables can be laid in along an entire wireway run. No pulling through of wires or cables is required with most designs.

7) PVC trunking/Raceways
As the name indicates these are the cable trays designed to carry cables like all other categories. These are made of Polyvinyl chloride(PVC) which is a synthetic plastic polymer. Generally in a data center environment, these are used in white space areas mainly as the pathways for fiber optic cables. These cable trays are considered as the most robust and effective method for fiber optic cablings.

8) Vertical Cable Management
Vertical cable management is when you run the cables from a piece of equipment within a server rack over to a vertical cable manager. This cable manager mounts within the rack and keeps cables bundled together while they travel up or down until they exit the rack. They come in several sizes so you can fit as many cables as you need to meet your specific situation. In addition, it allows the cables to bend safely when they exit the rack or go back toward another piece of equipment.
The advantages of vertical cable management are:
- Reduces Signal Interference – Vertical cable management strategies allow you to keep the power and data cables separate, which can help to prevent interference, thus improving signal quality.
- Cost Effective – The vertical cable managers are very affordable, and in most situations, you will only need one per server rack. This can help to reduce your overall expenses.
- Does Not Take Up Equipment Space – Since the vertical cable managers are placed along the inner edge of a server rack, it does not take up space that could be used for more equipment.
The disadvantages of vertical cable management are:
- Tracing Cables – If you need to trace out a cable, it is more difficult and may require that you carefully move each cable to ensure you are looking at the right one. Proper cable labeling, however, can offset this disadvantage.
- Adding & Removing Cables – Adding and removing cables can be a challenge, especially as the vertical cable manager starts to fill up. As long as you keep the cables neat and secured in place, this shouldn’t be a problem.

9) Horizontal Cable Management
Horizontal cable management is when you run the cables through a plastic or metal unit that is placed above or below the device where the cables are plugged. The cables are kept in place and separated so each one has its own spot within the cable manager. These cable managers can come in 1U or 2U size options so they can organize cables from multiple devices.
The advantages of Horizontal Cable Management include the following:
- Easier to Trace Cables – Since each cable runs through its own ‘port’ on the horizontal manager, it is far easier to trace cables. This is critical for troubleshooting problems.
- Adding Cables is Easy – Running new cables is very simple when using a horizontal cable manager. Just bring the cable up to the manager and run it through and into the port on the equipment. There is no worry about disrupting the other cables or other issues.
- Front & Rear Cabling – The horizontal cable managers can help to secure and organize cables that go to the front or the rear of the server rack. This can help ensure cables are protected and organized at all times.
The disadvantages of horizontal cable management include:
- Taking Up Space – The horizontal cable managers are mounted in a place that could otherwise house additional equipment. Excess use of this would result in wastage of rack unit spaces.
- Longer Setup – Running each cable through its own opening in the horizontal cable manager can be time-consuming. However, it is worth the effort to have a properly organized server rack.

Summary
Data centers are having a huge amount of cables to be managed and the cable trays used in this building will be a combination of multiple types of trays. The choice of material for any particular installation depends on the installation environment (corrosion and electrical considerations) and cost. Cable trays are available in a wide range of straight segment sizes and include splices, connectors, brackets, cable guides and supports, allowing specifiers to piece together a solution that will meet their specific needs. We should first make sure a cable tray meets our requirements, according to the type of cable(electric cables or network cable) that will be used and whether it will be bundled or separate. Additional factors include the bend radius of cables, connection points, mounting requirements, ease of installation and removal, as well as accessibility above or below the raised floors.
Have a comment or points to be reviewed? Let us grow together. Feel free to comment.