Shielded Twisted Pair(STP) and Unshielded Twisted Pair(UTP)
As we all know that there are two types of data transmitting medium available on the market which are copper twisted pair cables and fiber optic cables. We want to make use of both of these cables in a network environment and one of the most widely used cables is Twisted-pair cables which we cannot deny. Twisted-pair cables are a pair of wires that forms a circuit that can transmit data. The pairs are twisted to provide protection against crosstalk, the noise generated by adjacent pairs. I believe that this really makes sense for you too, right? Let us understand the application of these in a network environment.
Cables selection for the network operation is mainly based on below criteria,
- Bandwidth required
- Overall length of the channel
- Types of transceiver
- Environmental conditions
- Future growth considerations
Since we know that the major function of twisted pairs is to avoid cross-talk and noise there is some technology advancement in this area which will help you to choose the cable. This improvement is based on shielded and unshielded solutions and this is the differentiation factor of twisted-pair cables.
Noise and Cross talk cancelation of twisted-pair cables
The main purpose and creation of twisted pair cables are its capability to cancel noise and cross-talk by its design itself. Let us understand that basic principle first,
A pair of wires forms a circuit that can transmit data. When an electrical current flows through a wire, it creates a small, circular magnetic field around the wire. When two wires in an electrical circuit are placed close together, their magnetic fields are the exact opposite of each other. Thus, the two magnetic fields cancel each other out. They also cancel out any outside magnetic fields. Twisting the wires can enhance this cancellation effect. Using cancellation together with twisting the wires, cable designers can effectively provide self-shielding for wire pairs within the network media.
Let us look into different types of copper twisted-pair cables in detail. In accordance with international ISO/IEC 11801:200 Standard one should use a special code letter to designate one or another type of cable.

You can see various short names here which will help you to easily understand below cable types. Let us have a look into each of these in detail.
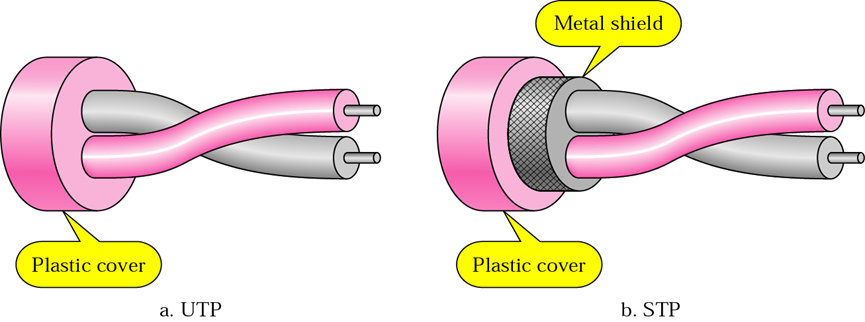
UTP or U/UTP(Unshielded Twisted Pair)
Just the name explains there are no shields around it to prevent the electromagnetic environment. This is the most common CAT 6 cable that we are seeing on these days. The UTP cable consists of a pair of wires twisted together. The default design of a twisted pair cables is providing some electromagnetic compatibility up to an extent and that is the only prevention against the electromagnetic signal.

Shielded Twisted Pair(STP)
You might have seen one of the network cable selection criteria in a data center is environmental factors. So what are the factors that could be leading to this?
One of the major factors that can affect or corrupt the data transfer is due to electromagnetic interference. Electromagnetic interference, or radio frequency interference, is when an electromagnetic field interrupts or degrades the normal operation of an electronic device. Such interference is generated on a small scale by everyday items ranging from cellular phones to fluorescent lights. Large sources of interference, such as telecommunication signal facilities, airports, or electrical railways, can interfere with data center servers and networking devices if they are in close proximity.
There are multiple ways to prevent this electromagnetic interference across all platforms, let us look into the prevention that we can take care of in network cabling. Hence the selection of copper twisted-pair cables can be in accordance with your environment. Hence the selection of copper twisted-pair cables can be in accordance with your environment.
F/UTP (FTP)
As the letters indicate an overall foil shield (F) with unshielded twisted pairs (UTP) is the structure of this cable. These cables are with general outer shielding made of aluminum foil, which is the basic protection from external noises.

SF/UTP
Both an overall braid screen (S) and foil shield (F) with unshielded twisted pairs (UTP). This cable is also occasionally referred to as an STP cable. The shielding of this cable consists of two layers the inner layer is made of aluminum foil and the second (outer) one is made of tinned copper braiding.

U/FTP
No overall shielding or braid (U) with foil screened twisted pairs (FTP). This cable construction denotes that each pair has its own individual shielding without the general one. Besides outer external interference, this way of shielding also prevents the cable from the crosstalk between pairs. This type of shielded cable is commonly used in CAT 6 and above and 10GBaseT applications as well.

F/FTP
An overall foil shield (F) with foil screened twisted pairs (FTP).
This cable has both general shielding and individual shielding for each pair made of aluminum foil. Such double shielding provides maximum protection from interference. Similar to F/UTP cables, these shielded cables are commonly used in 10GBaseT applications.

S/FTP
An overall braid screen (S) with foil screened twisted pairs (FTP). Here the cable with individual shielding of each pair is made of aluminum foil and general shielding made of tinned copper braiding. Such construction combines all advantages of both shielded types and provides excellent protection at all frequencies. It is applied in 6A, 7, 7A and 8 Categories. Besides, such shielding is useful in case of twisted pair cable is laid near the power cable.

In conclusion, you have understood the different types of cables that you can choose to avoid electromagnetic signal interference. You have to select the cable as per your environment with the understanding that how far you need to select this. I would like to add, that twisted pair cable will be relevant and demanded for a considerable time despite the fact that data transmission technology is rapidly evolving day by day and getting more and more strict requirements to cable links. Over the past few years, the performance of twisted pair cable increased several times. Today the industry is already in the process of twisted pair cable development, which would be capable to transmit data at the rate of 100 Gbit/s.
Have a comment or points to be reviewed? Let us grow together. Feel free to comment.