BiDi SFP and Compact SFP Transceivers(cSFP)
If you are a person working on fiber optic cables and connectors, you must have at least heard about BiDI SFP connectors and used it. Have you ever think that why are these modules are having a single port? Is that because it can do either of transmitting/receiving? If not, how does it differ from traditional SFPs? What about the Compact SFP transceivers then? Is this more advanced to BiDi SFPs? Will these modules are going to replace the traditional SFP connectors? All of these questions will be answered in this article,
We have all mostly seen our SFP connectors with two separated ports. Whereas one is TX(laser) port which is used to transmit the signal, and the other one is RX(photodetector) port which is used to receive signals. This is the conventional two-fiber Bi-Directional communication. Undoubtfully we can say that these are the most used and successful formula which is still existing. When the time goes by there have been many requirements of adding more value to existing products and technologies in fiber optics. One of the questions was pretty simple, instead of using two fiber optic cables to send and receive, why can’t we use single optic cables to perform the activity? With the development of WDM technology, transmitting and receiving optical signals on separate wavelengths can be achieved through only one single fiber. If that is the case we need only a single port in SFPs which can also perform send/receive. This was lead to the invention of BiDi SFP transceivers. BiDi SFP transceiver is a compact optical transceiver module that uses WDM (wavelength division multiplexing) technology and is compliant with the SFP multi-source agreement (MSA).


For bi-directional transmission technology, “bi-directional” is meant in sense of using optical fiber in two directions, similar to the use of single railway track in two directions. BiDi technology allows transceivers to both transmit and receive data to/from interconnected equipment through a single optical fiber, thus saving optical fiber resources and doubling your network capacity.

Unlike traditional optical transceivers, BiDi optical transceivers are fitted with wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) diplexers, which combine and separate data transmitted over a single fiber based on the wavelengths of the light. For this reason, BiDi transceivers are also referred to as WDM transceivers.
Working Principle of BiDi SFP
The difference between BiDi transceivers and the two-fiber optical transceiver mainly lies in that BiDi transceivers are fitted with WDM couplers, also known as diplexers, which help to combine and separate data transmitted over a single fiber based on the wavelengths of the light. BiDi transceivers are usually deployed in matched pairs to get the work most efficiently. And the diplexers of BiDi transceivers are tuned to match the expected wavelength of the transmitter and receiver that they will be transmitting data from or to.
There is two mechanisms that happen in the case of BiDi transceivers. Firstly, each signal which is sent/receive is operated in two different wavelengths. Secondly, bidirectional transceivers separate the two wavelengths into transmit and receive path with the help of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) diplexers. Look at the below picture to understand these two core concepts.

As you can see from the above diagram, the paired BiDi transceivers are being used to connect two devices. Device A is used to get upstream data, and Device B is used to get downstream data. Tx means to transmit and Rx means to receive. The diplexer in one transceiver (Device A) should have a transmitting wavelength of 1310 nm and have a receiving wavelength of 1550 nm. The diplexer in the other transceiver (Device B) should have a transmitting wavelength of 1550 nm and have a receiving wavelength of 1310 nm.
Advantages of BiDi SFP
This single fiber BiDi transmission gradually becomes a popular and cost-effective solution for today’s data center and IT infrastructure because of its unbeatable advantages such as,
(1) BiDi SFP modules integrate duplex data link over a single optical fiber.
(2) By utilizing BiDi SFP transceivers, the fiber cabling infrastructure costs could be reduced. With the reduction of fiber strands by half, the number of patch cords and patch panel ports can be reduced accordingly, as well as reducing the amount of tray space dedicated to fiber management
(3) Working with BiDi SFP optical modules, the capacity and reliability can be increased by simultaneously operating at more than one wavelength to transmit and receive on a single strand.
(4) BiDi SFP optical modules support a transmission distance up to 120km.
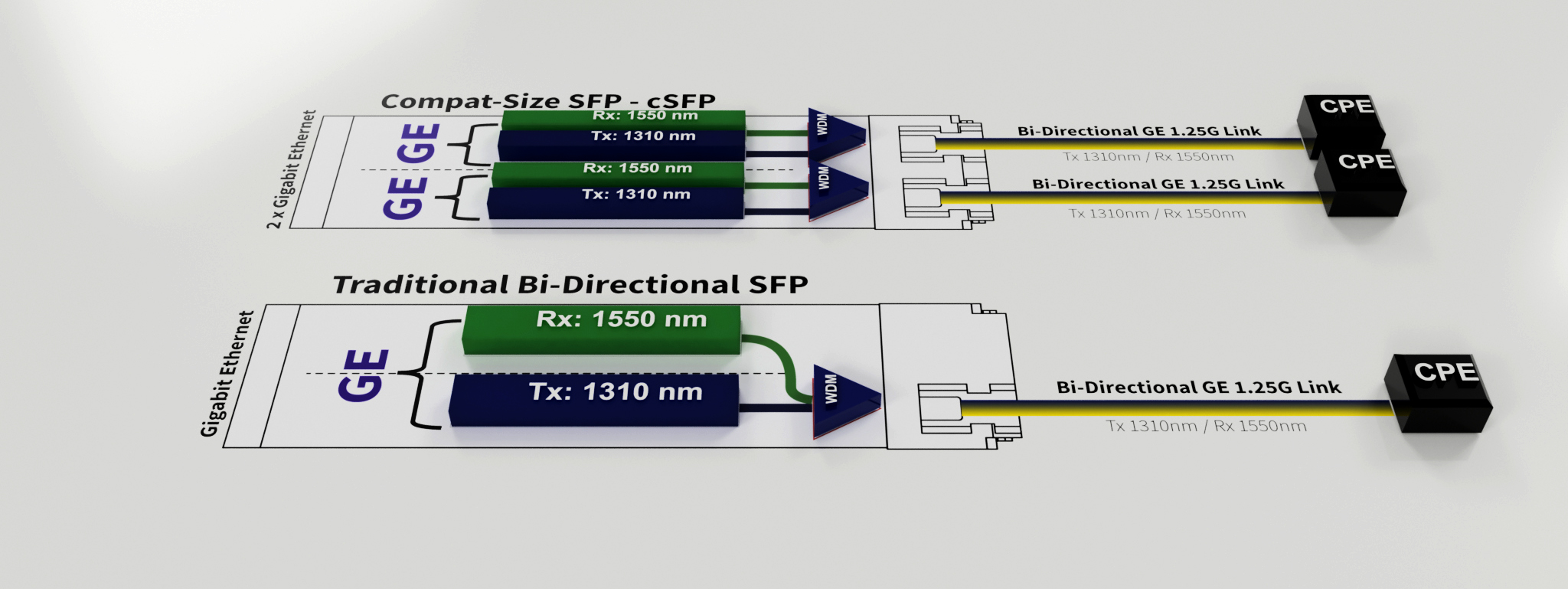
Compact SFP(cSFP)
The invention of BiDi SFPs has gone broader where we have to think about a situation where we can use the unused side of BiDi SFP ports, this was lead to the invention of Compact SFP. Compact SFP is a 2-channel BiDi SFP, which integrates two BiDi SFPs in one SFP module. Therefore, a compact SFP is also with two ports as the common SFP. The working principle of compact SFPs is the same as BiDi SFPs. The only thing which is required is that the equipment line card should supports cSFP and but the fact is that not so many vendors equipment has been designed to accept cSFP modules.
Compact SFP enormously increases the port density by combining two single fiber transceivers into one SFP form factor.


BiDi SFP and Compact SFP Connection Methods
For BiDi SFP, since it transmits and receives signals with different wavelengths, we should connect the two BiDi SFPs which have the opposite wavelength together. For example, we use a 1310nm-TX/1490nm-RX BiDi SFP at one end, then we must use a 1490nm-TX/1310nm-RX BiDi SFP on the other end (shown in the figure below).

The compact SFP (GLC-2BX-D) usually uses 1490nm to transmit signal and the 1310nm to receive signal. Therefore, the compact SFP is always connected to two 1310nm-TX/1490nm-RX BiDi SFP over two single-mode fibers (shown in the figure below).

Applications of BiDi SFP & Compact SFP
At present, BiDi and Compact SFPs have used in FTTx deployment P2P (point to point) connection. For example, in an FTTH deployment, optical fibers are used directly to connect the central office and the customer premises equipment. But because of the use of P2P architecture, the customer premises equipment has to be connected to the central office on a dedicated fiber. Thanks to BiDi SFP, which allows bi-directional communication on a single fiber by using wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), the connection between central office and customer premises equipment becomes more simple. Besides this application, BiDi SFP can be also applied in WDM fast Ethernet links, metropolitan area network, and inter-system communication between servers, switches, routers, OADM, etc.
Summary
BiDi and Compact SFPs are breaking the rules of traditional SFP modules in many aspects, which have been discussed in the above part. The biggest valuable advantage of these SFPs are that it can save cost on optical fiber, especially in long-haul fiber optic transmission. These transceivers in fiber cabling infrastructure reduced the costs by reducing the number of fiber patch panel ports, reducing the amount of tray space dedicated to fiber management, and requiring less fiber cable. Although BiDi transceivers cost more compared with traditional two-fiber transceivers, the cost savings of utilizing less fiber is more than enough to offset the higher price of them. And believe it or not, with the development of technology, it will have a broad market prospect.
Knowledge Credits: www.fs.com
Have a comment or points to be reviewed? Let us grow together. Feel free to comment.