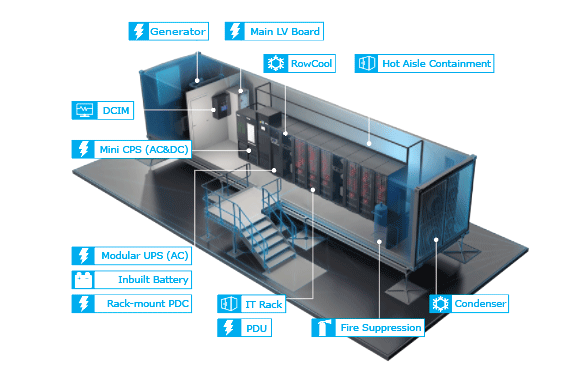
Prefabricated Data Centers(Modular & Containerized Data centers)
Prefabricated data centers have been an emerging technology that is largely adopted by enterprises and expected to grow more and more in the future. Read through below article to understand what is the prefabricated data centers and its various types(Modular Data Centers & Containerized Data Centers)
Due to the growth of large scale data handling, the data centers have emerged a lot for its needs and requirement. The cloud computing has become one of the emerging technologies in these years and it keeps growing which straightly depends on data centers. An average time period required to build data centers is calculated between 2-4 years or more and highly budgeted. As per the current requirement of data centers and usages, this is such a long time and involves a huge budget. How can we reduce this time period and budget without compromising the quality? The answer is Prefabricated Data Center Solutions.
In the past few years, the prefabricated modular building technology has become one of the most promising choices for the building industry and is widely applied in high-rise offices, dormitory and chain hotels. Considering the customer benefits such as quick construction, energy-saving, standardized production and predictable quality this was innovatively introduced into an information and communications technology (ICT) industry, building high-standard datacenters without brick-and-mortar. Prefabricated data centers are often marketed as converged infrastructure(way of structuring an information technology (IT) system which groups multiple components into a single optimized computing package), promoting economies of scale and efficient energy usage, including considerations regarding the external environment.
These systems consist of purpose engineered modules and components to offer scalable data center capacity with multiple power and cooling options. Prefabricated Modular Data Center Solution integrates power, cooling, firefighting, cabling and management systems into the prefabricated modules. All modules including IT, power, cooling, battery and multi-function modules are prefabricated in the factory, and all facilities will be pretested before delivery. The site preparation is synchronized with the module prefabrication. When all modules arrive at the site, it takes only a few days to complete all installation and commissioning.
Types of prefabricated data centers
Prefabricated data centers typically come in two types of form factors. The more common type referred to as Containerized data centers(portable modular data centers) and Modular data centers that can be quickly built on a site and added to as capacity is needed.
Containerized data centers(Portable data centers)
A containerized data center, as its name suggests, is a packaged data center solution that has been pre-engineered at the factory. It has been put together in an ISO container (20 feet by 8 feet or 40 feet by 8 feet) for shipping by sea. Also, it may be modified in a number of ways to better support the secure and practical use of IT equipment. A containerized data center system is a portable method of deploying data center capacity. A modular data center can be placed anywhere data capacity is needed. The basic requirement that most of these containers are designed to support includes servers, storage, and networking gear. In addition, containers may be designed to support some combination of uninterruptible power supply (UPS), generators and/or chillers, with some of that equipment supported in the same containers as the servers and storage equipment, or in separate and distinct containers.
Containerized data center solutions are designed to support three major modules of the data center which are said to be for IT space, Power and Cooling.
Containerized IT Space
A containerized IT space is a self-contained module consisting of compute, storage, and networking resources, designed to fit into a shipping container. Local experts build and configure from one to several racks of equipment inside a container, and the container is then shipped to a remote location to serve a specific set of customers, or to take advantage of lower space, power, and cooling costs. It also houses the support infrastructure to distribute power and air to those systems, as well as provides a suitable work environment for the IT staff that must operate the space. Typically, such a module incorporates the following subsystems,
- IT racks to hold the IT equipment
- Power distribution units (PDUs)
- Rack PDUs
- Air distribution system (CRAHs, CRACs, air ducts, depending on architecture)
- Humidification / dehumidification system
- Cabling infrastructure/cable management
- Fire detection / protection
- Lights
- Security systems

Unlike traditional data centers where there is one core layer and all of the resources are managed as a whole, modular data centers use a distributed core architecture. These containerized data centers can deliver flexibility, reliability, and scalability at a lower cost.

Containerized Power
A prefabricated power module is designed to provide bulk power to the data center. It may power a modular IT space or a traditional IT space within a building. The typical subsystems within a power facility module are switchgear/switchboards, ATS, UPSs with batteries, transformers, and panelboards. In addition, support systems such as lighting, security, cooling may exist in the module for enclosed form factors. Standby generators are generally a separate module that can be integrated with the power module.

Containerized Cooling
Today’s data centers use a range of cooling architectures to support the IT space, based on requirements for cost, efficiency, reliability, etc. The physical location (climate) of the data center is also a big driver when determining the optimal approach. The below picture illustrates a hydronics module consisting of pumps, VFDs, management, and connections for an air-cooled chiller modular design.

However, it’s not necessary that a data center must have all these three modules to operate. It depends on the data center type that customers needed(Enterprise, Co-location, etc.). They can either choose any single module or combination of these. If you do not opt for all these modules together then the rest of those functions must be operated with the traditional way of supply. Hence based on the configurations of the data center, it can be three types,
Semi-prefabricated – A data center comprised of a combination of prefabricated functional blocks and traditional “stick-built” systems
Fully prefabricated – A data center comprised completely of prefabricated IT, power, and cooling modules
All-in-one or Core– A data center that is self-contained in a single enclosure, with IT, power, and cooling systems.

On high scale data centers(enterprise data centers), there will be the utilization of multiple containerized IT spaces, power, and cooling. However containerized data centers are mostly seen on a small scale project, remote location( oil rigs, nuclear plants, war zones, etc.) or temporary projects, it’s not necessary to have huge infrastructures to support this. This could be used as the best solution.
Building blocks of Containers
One of the questions that we may have is, when we considering the containerized data centers, how efficient it will be to protect the data center from outside environments. Isn’t It essential for data centers to guarantee the stable operation of the critical business? All the Datacenter solution provides offer high reliability to customers. With IP55 protection-rating (optional IP65), these can withstand sand and dust storms, and heavy rain attacks. These containers may go under the salt-mist UL test and have strong anti-corrosion ability. Its service life is as long as 25 years. With customized coating, facade, and roof, the service life will be extended to 40 years. The solution passes a 120-minute fire test of a UL Lab and can withstand earthquakes of Mercalli 9 degrees. It can operate stably between -40℃~+55℃. These tangible benefits will help the data center easily adapt to all types of tough environments.
Advantages of Containerized data centers
Containerized modular data centers are the best solution for locations that might not be suitable for a building or another structure. But that’s not limited to this, there are several key advantages to a containerized data center,
Scalability – A containerized data center approach allows the total computing power to be scaled up by simply adding more containers. Each module plugs into the architecture like a Lego block. You don’t have to schedule a maintenance window to add capacity (or provision unused and expensive spare capacity) as you would in a traditional data center, which can cost thousands or even hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on which applications you’re running. In a high-frequency trading application or a Web 2.0 gaming portal, for example, downtime is extremely expensive.
Density and PUE – Density in a traditional data center is typically 100 watts per square foot. In a modular solution, space is used very efficiently and features densities as much as 20 kilowatts per cabinet. The PUE can be determined at commissioning and because the module is pre-engineered and standardized the PUE’s can be as low as 1.1–1.4. The PUE metric has also become a great gauge of data center green efficiency. Look for a provider that strives to break the 1.25 –1.3 barrier or at least one that’s in the +/- 1.2 range.
Troubleshooting – In a modular data center approach, faults are confined to each data center module, so it is easier to isolate problems and diagnose them. Containerized data centers are designed to be maintained by simply replacing a bad server or storage array or a (partial) rack, so there is less expertise required to perform on-site maintenance at a remote location than there is in a conventional data center.
Reliability – Because the containerized approach creates and leverages several self-contained data center modules, a total failure of the core in one module does not bring down the entire infrastructure, as it would in a traditional data center.
Less Capital Investment & Maintenance cost– The prefabricated modular datacenter solution saves about 40% initial investment compared with the brick-mortar building way, which brings quicker ROI to customers. Each container uses its maximum space by utilizing for its needs. The cost savings could also extend to software/management upgrades.
Disadvantages of Containerized data centers
If prefabricated modules offer flexibility, shorter time of deployment, and cost advantages, then why aren’t prefabricated modules a solution for everyone? Consider some of the challenges that prefabricated modules can present,
Existing investment in a building – When evaluating prefabrication for the IT space, it is important to note the existence or planned investment in a traditional building, as it will have a strong impact on the cost analysis. Since a prefabricated module already has a weatherproof shell, the added cost of locating them in a “finished” space has minimal cost-benefit.
Physical risks – Prefabricated modules can be exposed to outside elements such as severe weather, malicious intent, vehicle traffic (if placed in a parking lot), and animal insect infestation. Risks for a particular site should be assessed before choosing to deploy prefabricated modules. In these cases, similar considerations must also be made for other support systems, such as generators, chillers, or condensers.
Restrictive form factor – Prefabricated modules are large and heavy, and although mobile, they do present some challenges when it comes to placement and relocation. Modules may be too heavy to place on the roof of a building or may present logistical challenges in tight city streets.
Local code compliance – Since prefabricated modules present new technology, local municipalities may not yet have established guidelines for restrictions on modules. Inconsistencies could exist regarding how different municipalities classify power, cooling, and IT modules. Local codes impact the level of module engineering and customization required to secure Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ) approvals.
Transportation – The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) stipulates width (11.6 feet, 3.5 meters) and length limitations in many countries in order for truck and train loads to pass over curved roads, under bridges, and through tunnels. Outside of city tracks, roads can be even smaller, further restricting the mobility of containers. Non-standard wide loads require special permits and in some cases escorts which increases the cost of transporting the prefabricated modules.
Lesser Customization – Most of the prefabricated structures are designed and manufactured based on common market requirements. However many of the data centers may have their own requirements and designs to be accomplished. This can be a challenge here which makes these solutions less customizable.
Appearance – Containerized solutions without any esthetic adjustments may give off an air of “job site” to the location, making them unattractive for enterprise data centers or for providing services to third parties.
It is important to remember that a data center facility has but a single purpose — it is a means to an end, designed to house, protect, and support IT hardware so that applications can deliver services key to the organization and their customers. Consequently, when considering a containerized or modular systems, remember that while such systems may have been originally developed as a stop-gap measure to deal with an older facility’s capacity limitation, you need to examine your facility’s current plans and IT architecture to evaluate how well their use may relate to your organization’s long-term business strategy and goals.
Modular Data Centers(MDC)
This idea was almost similar to prefabricated buildings. Customers like to build data centers themselves – modular gives them that flexibility. Modularity is being able to build a data center piece by piece. A modular datacenter facility is constructed with a set of building modules of different types of functionality to form an entire data center facility having a standardized pre-approved architectural design and layout. All instances of a particular type of building module will have approximately the same floor plan and architectural design. In fact, we can say that modular data centers are custom made in many cases. An initial set of building modules can be built upon a parcel of land, and then as needs of space and additional capacity of the modular datacenter facility increase, then at a future point in time, additional building modules of the different types can be rapidly added to the initial set of building modules. The building modules of the different types use one or more connecting corridors architected into at least a first type of building module and corresponding aligned doorways between both building modules to interconnect two building modules adjacent and abutted to each other. Modular data centers(MDC) are often referred to as “Truly modular building data center facility“.

These models are not having much differentiation with traditional data centers. The vendor will design and manufacture the components as per the client’s preapproval in their factory. Modular data centers(MDC) may be based on components of modular blocks, pre-assembled and factory tested and provide a scalable solution and a delivery time that is shorter than in traditional brick and mortar construction. Once all these modules are ready, these components are shipped and delivered onsite on a ready to bind together style. Hence we can club all these and start the operations on a much lesser time period cost. Its major difference in relation to a containerized solution is that there is not a limited capacity for the number of racks or the total power for the IT load, but they may be assembled and dispatched in modules that have the right dimensions to ease shipping and transportation. This is the prefabricated structure that is largely adopted by enterprise data centers due to its customizability.
The main factor that is boosting the use of prefabricated modular solutions is the implementation times. The reason is that standard components are used that have been preassembled and tested at the factory and delivered and placed into commission on site. They provide reliable, efficient solutions with a very good “time to market” and the modular blocks may offer greater scalability, ease of replacement or field upgrades. The esthetic appearance is much more pleasing and customizable in modular solutions, making them more appropriate for enterprise data centers since, once they are assembled on-site (and even painted), they may look similar to a traditional data center.
Looking at the below video can give you practical ideas in a few minutes.
Do you want to know how these things are set up within a container? Looking at the video of Delta InfraSuite Datacenter solution and DataXenter – building modular Data Centers is the best that you can review.
Traditional data center Vs Prefabricated data center
Now we have seen the prefabricated data centers and their types. Now the question would be is this really better than our traditional data centers? Comparative studies would give you a much better answer for you.

Major Players
There are many major players on the ground with the solutions of prefabricated modular data centers. Some of them are as below,
- IBM Corporation – IBM Prefabricated Modular Data Center
- Cisco Systems Inc. – Cisco Containerized Data Centers
- Dell EMC – Dell EMC Modular Data centers
- HPE Company – HPE Modular Data centers
- Cannon Technologies Ltd. – Cannon Modular Data Centre Solutions
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd – Smart Modular Data Center
Summary
Two of the biggest reasons typically listed for the problem with data centers are capital and speed of deployment. The traditional brick and mortar data center takes a lot of money and time to build. Furthermore, the quick evolution of supporting technologies further entices organizations to work with fast and scalable modular designs. Outside of those two primary drivers, there are many benefits and reasons listed for why a modular data center approaches are emerging. However, the specific business needs should be analyzed as they relate to the project’s and the client’s needs based on the possible traditional construction scenarios and or prefabricated solutions, including their pros and cons, to decide which better matches and most appropriately satisfies the requirements and needs. Each data center project is unique so there is no applicable rule when choosing the possible implementation scenario.
Knowledge Credits: www.datacenterknowledge.com, www.schneider-electric.com
Have a comment or points to be reviewed? Let us grow together. Feel free to comment.